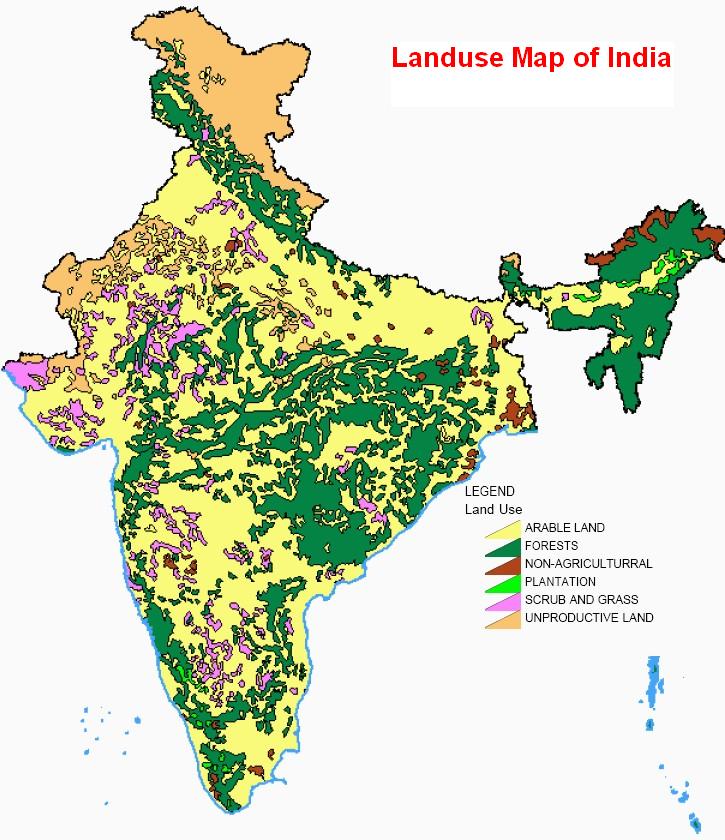
Describe the Various Land Uses in India
528 2018 est permanent crops. In India the Land Utilisation patterns can be classified into seven categories.

Land Revenue Systems In British India Zamindari Ryotwari And Mahalwari Clearias
Mountains plateaus plains islands and many more.
. 42 2018 est permanent pasture. One of the major reasons was the unequal distribution of land. Secondly quality of land has a critical bearing on agricultural output per unit area while it is of marginal.
Utilisation of land Land resources are used for the following purposes. Land reform is a broad term. Much minerals are also available.
Residential Land Use - where people live houses apartment buildings 2. Under it land in India is now classified under nine different categories viz i forests ii barren and unculturable land iii land put to non- agricultural uses iv culturable wastes v permanent pasture and other grazing land. About 517 of the total land is uncultivated waste which can be converted into.
The use of land is determined both by physical factors such as topography climate soil types as well as human factors such as population density technological capability and culture and traditions etc. Farming can be good to go in different climatic conditions as it provides two livelihood options with single land. Land not available for cultivation a Barren and waste land b Land put to non-agricultural uses eg.
A single piece of land is here to support both arable and pastoral farming which is advantageous for increasing the yield of farms from both crops and rearing. Recognized need to protect and preserve critical areas for conservation and. India possesses an area which is just a fortieth of the total land area of the world supporting 197 million cattle and ranking first in the world for cattle population.
All humans need food so this is. Meaning of Land Reforms. These are the general uses of land.
Laying of roads and railway lines 4. 231 2018 est other. Let us make an in-depth study of Land Reforms in India- 1.
The identified population needs and requirement for various development purposes. The seven types of land uses are. 605 2018 est arable land.
The buildings used for various religious and social purposes give the settlements their distinctiveness. Meaning of Land Reforms 2. Land use data accounts for only 93 because for most of the north-east states land use reporting is not done.
India has land under a variety of relief features namely. Agriculture and horticulture 2. Recreational Land Use - for fun entertainment purposes parks Bowling place 4.
Solve any question of Resources and Development with-. Land use and land management practices have a major impact on natural resources including water soil nutrients plants and animals. In India about 5109 of the land is under cultivation 2181 under forest and 392 under pasture.
The use of land for agriculture depends on soil type irrigation facilities and climate. Land resources are used for many purposes. Built up areas and uncultivated land occupy about 1234 Kundra 1999.
Agricultural land which is used for growing crops and rearing animals is the oldest human use of land. Other uncultivated land excluding fallow land 4. The urban settlements are differentiated from the rural settlements on the basis of certain characteristics such as the size and density of.
Land requirement in terms of adequacy of land for food production settlement expansion etc. Institutional Land Use - government related schools town hall police station 3. The relevance of land for agriculture can be understood thus.
Namely 1 Net area sown2 Forest area3 Land not available for cultivation4 Fallow land5 Cultivable wasteland6 Permanent pasteurs and other grazing lands7 Land under miscellaneous uses1Net area sown- It includes land that can be used to cultivate crops. The pattern of agriculture is always irregular in IndiaIn the pre-independence era tenants peasants and small farmers suffered a lot due to the revenue systems of Mahalwari Zamindari ryotwari. 35 2018 est forest.
A container for holding water ADVERTISEMENTS. Land use Pattern in India. The establishment of British rule in south and south-western India brought new problems of land settlement.
Land Use Pattern in India. Land use information can be used to develop solutions for natural resource management issues such as salinity and water qualityFor instance water bodies in a region that has been deforested or having erosion will have different water quality. Major Landforms of India.
Which are the major landforms of India. The land area prone to floods has doubled from 20 million hectares to above 40 million hectares in the last ten years. Mountains The Himalayan mountain range is a major landform in India.
The settlements are generally divided into two types-urban and rural or towns and villages. This entry contains the percentage shares of total land area for three different types of land use. Firstly agriculture is a land intensive activity which means that it requires more land compared to non-agricultural activities in relation to the respective output.
Land that is not available for cultivation. Mining of mineral resources 6. Vi miscellaneous tree crops and groves not included in the net area own vii current fallows.
Objectives of Land Reforms 3. Other uncultivated lands excluding fallow land Net sown area. For fodder cattle grazing forest wealth for.
The purposes are mentioned below. Another group of landlords was created all over India when the government started the practice of giving land to persons who had rendered faithful service to the foreign rulers. On Agricultural Land use Changes in India.
The location of the different land use categories as follows. Buildings roads factories etc. It includes topography climate soil.
The land is used to grow crops to cultivate fruits and develop fisheries. 164 2018 est Definition. And ix net area sown.
Land use depends upon the following factors. Population density Technological capability Culture Traditions etc. It refers to an institutional measure directed towards altering the existing pattern of ownership tenancy and management of land.
Open Vacant Space. Land Reforms in India. Total area of India is 328 million km2.
It borders on the Northern part of India and protects the country from foreign invasions. Agricultural land forest and other.

Difference Between Urban And Rural In India Their Comparisons
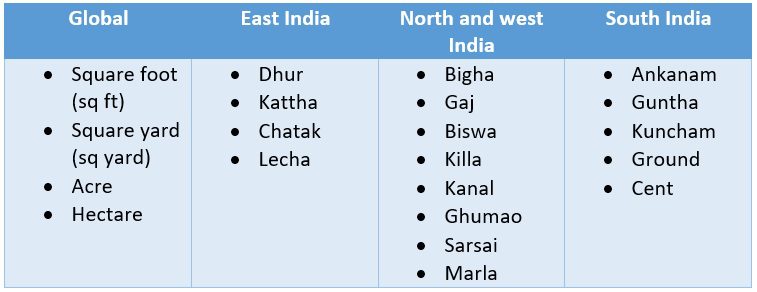
Common Land Measurement Units In India Housing News

India Rapeseed Mustard Growing Areas Map Indian Agriculture Maps Area Map Map Geography Map

Proposed Land Use Zoning Of Metropolitan Development Plan 2031 For Hyderabad Metropolitan Region Hyderabadrealt Master Plan How To Plan Graphics Inspiration

Physiographic Map Of India India Physiographic Map India Map India World Map Map
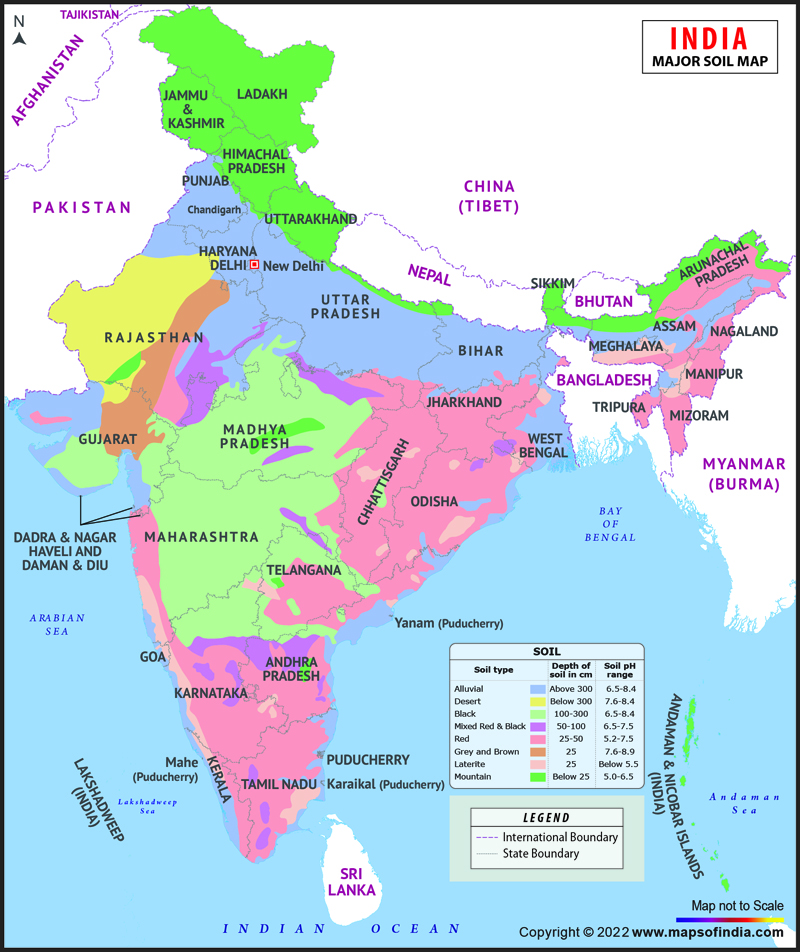
Soil Map Of India Define Types Of Soils In India

Istanbul 2000 And 2020 Istanbul 2000 Environment Agency

Land Use Pattern In India Social Science Soil Conservation Appropriate Technology
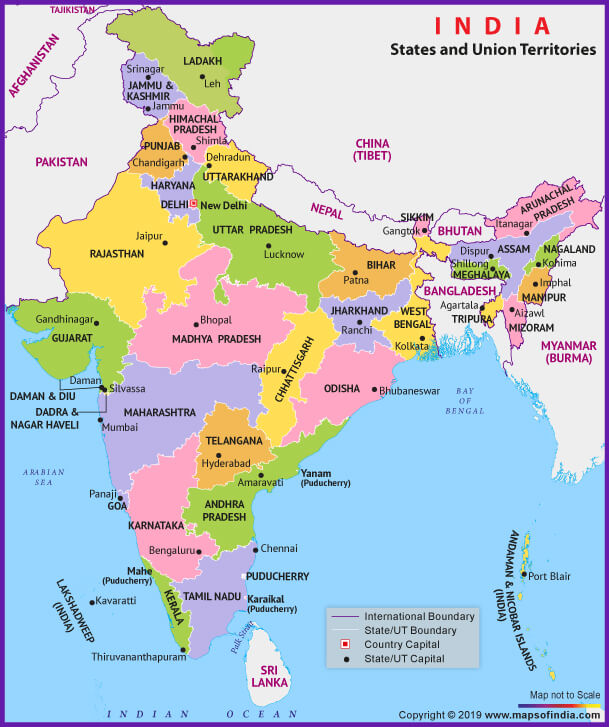
India Know All About India Including Its History Geography Culture Etc

Land Use Map Of India National Institute Of Hydrology India Water Portal

Why India Wins Tourists Heart Tourism India Tourist Travel And Tourism

Common Land Measurement Units In India Housing News

What Is The Difference Between Land Cover And Land Use

Amazon Com India Map 36 W X 40 69 H Office Products

Bigha In India Area Converter And Faqs Housing News

River Map Of India Major Indian Rivers Map Whatsanswer In 2021 Indian River Map India Map India World Map

Land Use Pattern Of India India Facts Relief Geography India

Agribachelor Agriculture Types Of Agriculture Agriculture In India Imporatance And Their Crops Types Types Of Agriculture Agriculture In India Agriculture
Comments
Post a Comment